In medical billing, modifiers play a crucial role in ensuring claims are processed accurately and reimbursements are made correctly. A modifier is a short code added to a CPT or HCPCS procedure code to provide extra details about the service performed, such as whether it was done on both sides of the body, repeated, or distinct from another procedure. These small codes carry big financial importance, as incorrect or missing modifiers often lead to claim denials and payment delays. Understanding modifiers in medical billing helps healthcare providers maintain accurate documentation, support compliance, and ensure smooth reimbursement cycles.
Table of contents
- What Are Modifiers in Medical Billing?
- Types & Categories of Modifiers
- Common Modifiers and Their Meanings
- Why Modifier Mistakes Lead to Denials & How to Avoid Them
- Best Practices for Using Modifiers Correctly
- How Practice Perfect Supports Providers With Modifiers & Billing Accuracy
- Final Thoughts
- Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Modifiers in Medical Billing?
Understanding modifiers in medical billing is essential for accurate claim submission and smooth reimbursement. Modifiers act as clarifiers that tell the payer the “how” or “why” behind a procedure.
Definition & Purpose
A modifier is a two-character code, numeric or alphanumeric, added to a procedure code to provide additional context about the service rendered. It explains how a service was performed, if it was repeated, bilateral, or distinct from another procedure.
For example:
- Modifier 25 indicates a separately identifiable evaluation and management (E/M) service performed on the same day as another procedure.
- Modifier 59 denotes a distinct procedural service, showing that two procedures should be paid separately.
The main purpose of modifiers is to ensure that claims reflect the complete story of a patient encounter. They help payers understand what was done, why it was necessary, and how it was performed, all without altering the main service code.
How Modifiers Affect Claim Processing & Reimbursement
Modifiers directly influence how insurance companies evaluate, price, and reimburse claims. When applied correctly, they:
- Clarify service details: Provide transparency about the scope or uniqueness of a service.
- Prevent duplicate denials: Indicate that similar-looking codes represent separate procedures.
- Support accurate payment: Ensure the provider is reimbursed for the full value of work performed.
- Enhance compliance: Demonstrate proper documentation and adherence to payer rules.
For instance, adding modifier 50 (Bilateral Procedure) tells the insurer that the same procedure was performed on both sides of the body, allowing payment for the full service. Without it, the payer may assume duplication and deny part of the claim.
Risks of Using Incorrect or Missing Modifiers
Incorrect or missing modifiers can lead to significant financial and compliance challenges. Common risks include:
- ❌ Claim denials or rejections: Missing or mismatched modifiers trigger automated payer denials.
- ⚠️ Underpayments: Without proper modifiers, the insurer may pay less than the actual service value.
- 🧾 Compliance issues: Repeated misuse of modifiers can raise red flags during audits.
- ⏳ Delayed cash flow: Reworking denied claims consumes time and resources.
For example, using modifier 59 where modifier XU is more appropriate can confuse or trigger a denial under payer-specific guidelines.
👉 You can read more about related issues in our blog on Top 10 Denials in Medical Billing.
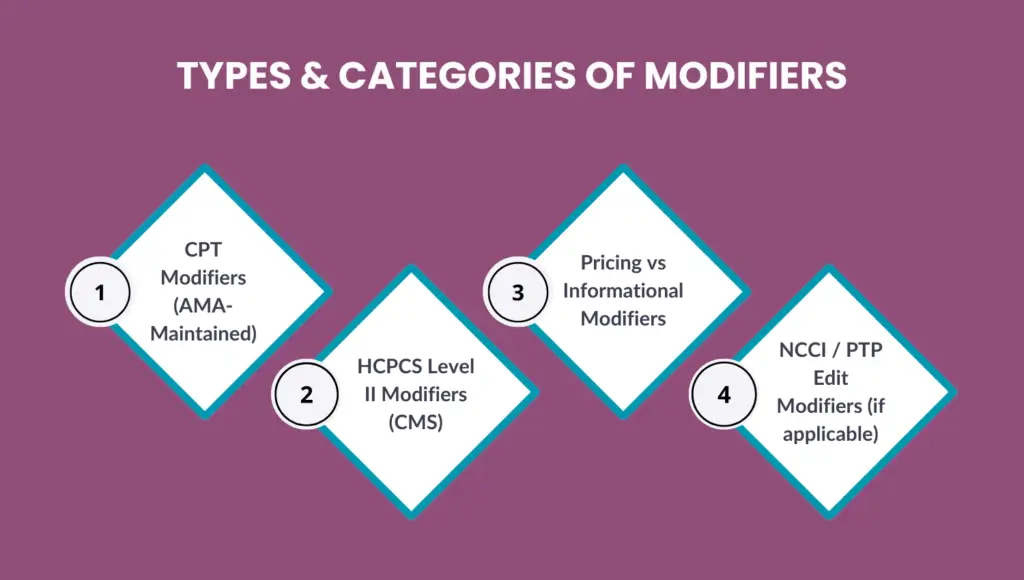
Types & Categories of Modifiers
Modifiers are not all the same. Each serves a distinct purpose and is governed by different coding systems. Understanding these categories helps ensure your claims are billed correctly and comply with payer rules.
CPT Modifiers (AMA-Maintained)
CPT (Current Procedural Terminology) modifiers are maintained by the American Medical Association (AMA). These two-digit codes are appended to CPT procedure codes to provide additional details about a service.
For example, modifiers clarify if a service was partially reduced, performed by more than one physician, or required greater effort than usual. Using CPT modifiers accurately helps providers avoid ambiguity and ensure compliance with payer policies.
HCPCS Level II Modifiers (CMS)
HCPCS Level II modifiers are maintained by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) and typically consist of two alphanumeric characters. These modifiers indicate supplies, ambulance services, or non-physician procedures not covered under CPT codes.
For example, modifier QK identifies medical direction by a physician for multiple anesthesia procedures, while JW denotes unused medication amounts. Accurate use of HCPCS modifiers is critical for clean claim submission and compliance with CMS regulations.
Pricing vs Informational Modifiers
Modifiers are often classified as pricing or informational:
- Pricing modifiers directly impact reimbursement amounts. For example, modifier 50 (Bilateral Procedure) can change how a claim is paid.
- Informational modifiers provide clarity but do not affect payment. For example, modifier LT (left side) simply specifies the location of the service.
Correct categorization ensures your claims are processed accurately without over- or underpayment.
NCCI / PTP Edit Modifiers (if applicable)
The National Correct Coding Initiative (NCCI) and Procedure-to-Procedure (PTP) edits define when certain code combinations are not allowed unless supported by an appropriate modifier.
Common examples include modifier 59 or its subset modifiers (XE, XS, XP, XU) — used to indicate distinct services that would otherwise be bundled.
Proper application prevents denials for unbundling errors while maintaining compliance with payer audit rules.
Common Modifiers and Their Meanings
Understanding frequently used modifiers ensures smoother claim processing and faster payments. Below are the most common ones every provider and biller should know.
Modifier 25 – When & Why Use It
Modifier 25 indicates a significant, separately identifiable Evaluation & Management (E/M) service performed on the same day as another procedure.
Example: A patient visits for a wart removal but also receives evaluation for a new rash. The E/M visit (99214) and the procedure (11730) can be billed together with 99214-25.
Incorrect use of modifier 25 can trigger audits or payer rejections, so ensure the documentation clearly supports the separate E/M service.
Modifier 59 – Distinct Procedural Service Explained
Modifier 59 identifies procedures that are not normally reported together but are appropriate under specific circumstances.
Example: If two procedures are performed on different anatomical sites or distinct sessions, modifier 59 clarifies that they are separate.
Example codes: 11042-59 + another code.
Use this modifier only when no other modifier more accurately describes the scenario (such as XE, XS, XP, or XU).
Modifier 50 – Bilateral Procedures
Modifier 50 is used when the same procedure is performed on both sides of the body during the same session.
Example: Bilateral knee surgery would be coded as 27447-50 instead of reporting the procedure twice. Accurate use ensures correct reimbursement — some payers may require separate claim lines rather than a single line with modifier 50.
👉 You can read more about: What Is AOB in Medical Billing and Why It Matters for Your Practice?
Other Frequently Used Modifiers
Here are some additional modifiers that are commonly applied in medical billing:
| Modifier | Meaning | Example Usage |
|---|---|---|
| 25 | Separately identifiable E/M service | 99214 + 11730 |
| 59 | Distinct procedural service | 11042-59 + other code |
| 50 | Bilateral procedures | 27447-50 |
| 26 | Professional component | 71045-26 |
| 22 | Increased procedural services | 19318-22 |
| 95 | Telehealth service | 99213-95 |
| 76 | Repeat the procedure by the same physician | 93000-76 |
| XS | Separate structure | 11055-XS |
| XE | Separate encounter | 11719-XE |
| XP | Separate practitioner | 45378-XP |
| XU | Unusual non-overlapping service | 20550-XU |
Using these modifiers properly ensures claim accuracy, supports medical necessity, and minimizes payer denials.
Why Modifier Mistakes Lead to Denials & How to Avoid Them
Even a single incorrect or missing modifier can cause claim rejections, payment delays, or compliance risks. Modifiers must always align with payer policies, procedure combinations, and documentation to ensure accurate reimbursements.
Common Modifier Errors
Some of the most frequent modifier-related issues include:
- Missing Modifiers – Forgetting to append a required modifier leads to underpayments or denials.
- Wrong Modifier – Using a CPT modifier where an HCPCS one applies (or vice versa) results in coding mismatches.
- Stacking Errors – Combining incompatible modifiers, such as 59 and 51 can make a claim invalid.
- Overuse of Modifiers – Unnecessary addition of modifiers without documentation support can raise audit flags.
Performing routine audits and validating all modifiers before claim submission helps prevent these costly mistakes.
Payer-Specific Rules & Documentation Requirements
Each payer—whether Medicare, Medicaid, or private insurance—has its own modifier usage policies. For example, some payers require specific X modifiers (XE, XS, XP, XU) instead of 59 for distinct procedures.
Proper documentation must always justify the modifier. Operative notes, physician statements, or progress reports should clearly describe why the service qualifies for a specific modifier. Staying updated with payer bulletins ensures your billing process aligns with current standards.
How to Appeal or Correct Modifier-Related Rejections
If a claim is denied due to modifier errors, don’t resubmit blindly. Instead:
- Review the payer’s denial reason code to identify the modifier issue.
- Check claim documentation to verify if the modifier was valid.
- Submit a corrected claim with the right modifier or supporting notes.
- Appeal with documentation if the service was correctly coded but denied incorrectly.
Your billing staff should maintain a clear workflow for denial review and appeal tracking. For detailed strategies, refer to our blog on Denial Prevention Strategies Every Practice Should Follow.
Best Practices for Using Modifiers Correctly
Proper use of modifiers not only prevents denials but also helps healthcare practices maintain compliance and optimize reimbursements. Here’s how to ensure accuracy every time.
Verify Modifier Necessity Before Submission
Before adding a modifier, confirm that it’s clinically and procedurally necessary. Review payer guidelines and ensure the service would be bundled or misinterpreted without it. Modifiers should clarify—not justify—billing for medically necessary services.
Maintain Accurate Documentation & Audit Trails
Every modifier used must be backed by documentation showing the medical necessity and distinct nature of the service.
Maintain:
- Procedure notes
- E/M visit documentation
- Operative reports
- Diagnostic details
Accurate recordkeeping builds a defensible audit trail and supports compliance during payer reviews or RAC audits.
Training Staff & Coding Teams on Latest Modifier Guidelines
Regular staff training is essential as coding guidelines evolve annually. Your billing and coding teams should receive updates on:
- AMA CPT updates
- CMS policy revisions
- Payer-specific edits
Consistent education ensures everyone applies modifiers correctly and identifies potential errors before claims go out.
Use Software Tools to Validate Modifiers Before Claim Submission
Modern billing software can flag incompatible or missing modifiers automatically. By integrating claim scrubbing tools and AI-driven validation systems, practices can:
- Identify duplicate or invalid combinations
- Match modifiers to correct CPT/HCPCS codes
- Ensure compliance with NCCI edits
This automation saves time, improves accuracy, and minimizes denials related to manual coding errors.

How Practice Perfect Supports Providers With Modifiers & Billing Accuracy
Accurate modifier usage is the backbone of clean claim submission and reliable reimbursements. At Practice Perfect, our billing experts specialize in modifier validation, compliance audits, and payer-specific coding accuracy — ensuring that every claim you submit is both compliant and optimized for faster payment.
Our team uses advanced claim scrubbing and automated validation tools to catch potential modifier issues before submission, helping providers avoid denials and revenue losses. We also provide periodic documentation audits to ensure modifier usage aligns with payer policies and coding guidelines.
Final Thoughts
Modifiers are powerful tools that communicate essential details about medical services — but when used incorrectly, they can be a leading cause of claim denials. By understanding modifier rules, validating their necessity, and maintaining strong documentation, providers can ensure clean claims, accurate payments, and regulatory compliance.
👉 Talk to a Medical Billing Expert today to optimize your coding accuracy and maximize reimbursement efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions
A modifier in medical billing is a two-character code added to a CPT or HCPCS procedure to provide extra information about the service performed, such as multiple procedures, distinct services, or unusual circumstances.
Modifier 59 is used to indicate that two procedures were performed independently and are not bundled together. It shows that the services were distinct and should be reimbursed separately.
CPT modifiers are maintained by the AMA and apply mainly to physician services and procedures, while HCPCS Level II modifiers are created by CMS and used for supplies, equipment, or non-physician services.
Review the payer’s remittance advice (RA) or explanation of benefits (EOB). It will include denial codes or remarks indicating incorrect or missing modifiers.




